The default mode Network
The Default Mode Network (DMN) includes brain areas in the cortex that are normally active during rest and is involved in remembering events, social and emotional judgment, and planning for the future. The DMN is often considered the opposite of the 'task-oriented' network, which is active during cognitive tasks and commands.
The DMN is one of the first brain networks to be identified using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), a technique that measures blood flow in the brain and can therefore indicate the activity of brain areas. The DMN is activated when the brain is not busy with specific tasks or commands, such as thinking about a problem or reading the news.
The DMN is one of the largest and most complex brain networks, and consists of several parts of the brain, including the medial prefrontal cortex, parietal cortex, temporal cortex, cingulate cortex, and hippocampus. These brain areas are involved in various cognitive functions, such as working memory, attention, emotion regulation, language and social cognition.
The medial prefrontal cortex, also called the ventral medial prefrontal cortex, is an important part of the DMN. It is involved in the regulation of emotions, self-reference and mental simulation. The parietal cortex is involved in the integration of visual, auditory and somatosensory information and in planning movements. The temporal cortex is involved in language, memory and auditory processing. The cingulate cortex is involved in emotion regulation and attention regulation. The hippocampus is involved in memory and emotion regulation.
View previous posts about it here Default Mode Network (DMN)
Depression and anxiety
Recent research suggests that the DMN is also involved in mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety disorders. Studies have shown that activity in the DMN is increased in people with these conditions. It is also thought that the DMN could be used as a biomarker for mental illness, as changes in the activity of the DMN can be used to determine the severity of the condition and measure the effectiveness of treatments.
Psychedelic drugs reduce activity in the DMN
Psychedelics, such as LSD and psilocybin, are substances that influence the functioning of the brain and can lead to altered consciousness and emotional experiences. These substances have been shown to reduce the activity of the Default Mode Network (DMN).
One of the ways that psychedelics can decrease DMN activity is by increasing communication between different parts of the brain that are normally less connected. This can lead to a reduction in the activity of the DMN, because the network is less necessary for processing information.
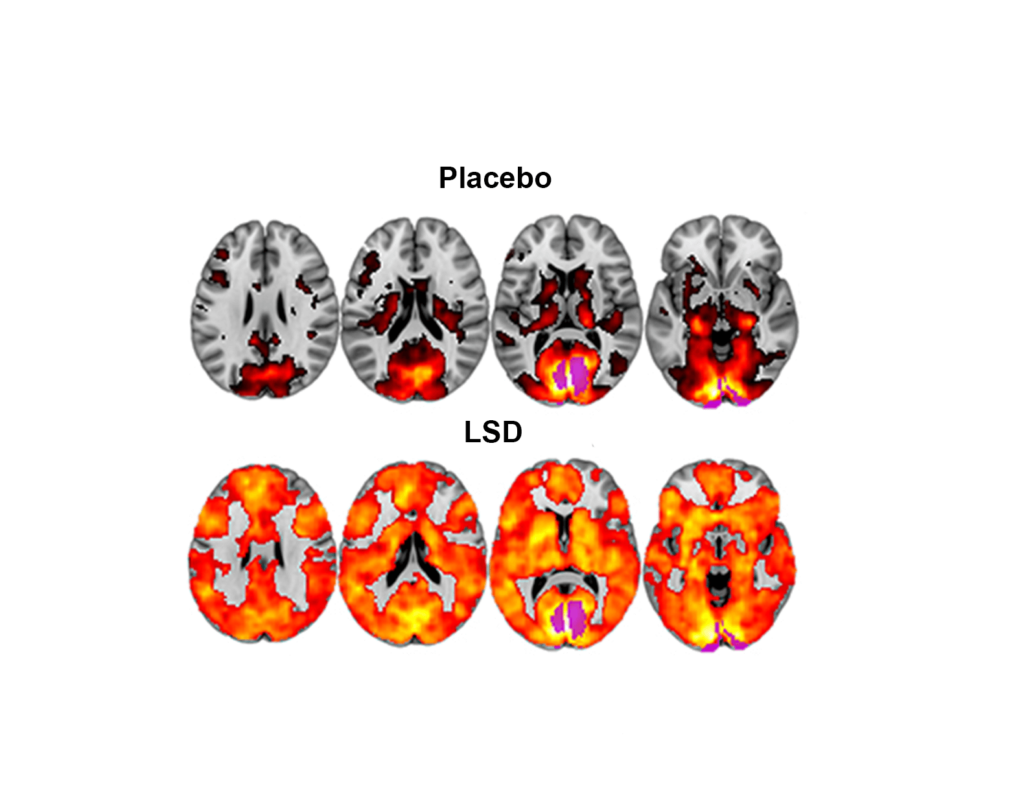
Another way that psychedelics can decrease DMN activity is by reducing blood flow in these brain regions. This can lead to a decrease in DMN activity.
There are also studies suggesting that psychedelics may decrease DMN activity by reducing the brain's tendency to "default" to familiar patterns of thinking and feeling. This can help to gain new perspectives and insights.
Less activity in the DMN via trip therapy
Give yourself more rest and enjoy being more in the here and now. Grab life with both hands. Life is not just about surviving, but especially about experiencing. Decrease activity of your DMN by making as many healthy choices as possible. Kickstart your life by using our support in healthy choices and a guided psychedelic session. The combination of a healthy lifestyle and psychedelic therapy works better than the individual components.
In order to undergo a trip therapy session, we must screen for health and safety. We do this through the intake. The intake will also form the basis for advice during the preparation for the psychedelic session. The intake can be found below via the link below: