Psilocybin and BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) are two substances that are involved in the regulation of brain function and behavior. Psilocybin is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in certain types of mushrooms, and it is thought to have antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. BDNF is a protein produced by the brain that helps to support the growth, development, and maintenance of neurons, and it is thought to play a role in learning and memory.
Some research has suggested that psilocybin may affect the levels of BDNF in the brain, and that this may be one of the mechanisms by which it produces its effects. For example, one study found that psilocybin increased BDNF levels in the hippocampus, a brain region involved in learning and memory, and that this increase was associated with improved mood and reduced anxiety in participants. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between psilocybin and BDNF.
Psilocybin is closely linked to BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor), a key protein responsible for promoting neuroplasticity — the brain's ability to form new neural connections and adapt to change.
When psilocybin is ingested, it’s converted in the body into psilocin, which strongly activates 5-HT2A serotonin receptors in the brain. This activation triggers a cascade of biochemical effects, one of which is the increased release of BDNF.
Higher BDNF levels contribute to:
- The growth of new neurons and dendritic branches.
- Enhanced learning and memory.
- Emotional resilience and faster recovery from stress or trauma.
- Greater cognitive flexibility — allowing for new insights and breaking old thought patterns.
These mechanisms help explain why many users of psilocybin-assisted therapy report profound shifts in perception, emotional healing, and a renewed sense of purpose after just one or two sessions.
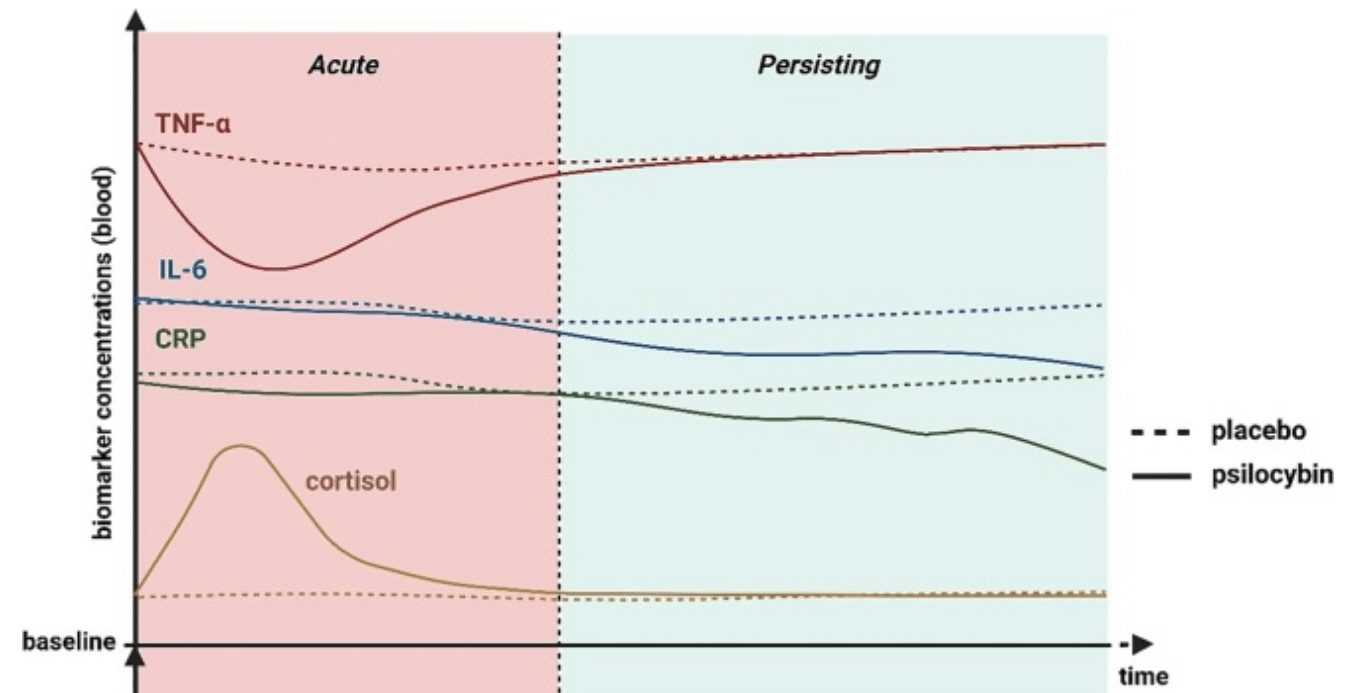
In addition, psilocybin has been shown to reduce inflammation in the brain by lowering markers like TNF-alpha, IL-6, and CRP. Chronic inflammation is often linked to depression, so this anti-inflammatory action may further support BDNF expression and overall mental health.
You can explore more on how psilocybin influences brain plasticity and emotional healing in this detailed overview of psilocybin therapy.