Information MDMA analogue
From 1 July 2025, we can no longer dispense MDMA analogue
On this page, we provide more information about the MDMA analogue we previously offered at Triptherapie as a legal alternative to harness the therapeutic effects of MDMA.
Find out what the risk profile is and what sessions we offer.
Disclaimer legislation
Opium Act
MDMA is an illegal drug that falls under the Opium Act (list 1). According to the Opium Act, the substances on list 1 hard drugs; substances that, according to the government, entail an unacceptably high risk and have no medical use. This means that the possession, production, sale and use of MDMA is punishable in the Netherlands. Because we use an analogue that is not mentioned on this list, we can legally work with this drug. According to current legislation, these MDMA sessions/therapy are not yet covered by the Medicines Act and are not medical treatment and therefore no reimbursement is possible through health insurers.
Experimental phase
MDMA, Ecstasy and analogues are widely used worldwide. Although most users experience no immediate problems, little scientific research has been done on its long-term safety. Long-term use of MDMA can increase the risk of depression, anxiety and memory problems. Much of this research is limited to animal studies, and few clinical studies on the safety of chronic MDMA use in humans have been conducted. According to studies among recreational users, MDMA is said to be safer than the use of other substances such as alcohol, cocaine and cannabis.
Which MDMA analogue?
It is not possible to provide the exact substance name of the MDMA analogue we use to protect its legal status. By giving the exact name it may be possible for authorities and law enforcement officers to place the substance on list 1 of the Opium Act. For this reason, the identity of the substance must be protected and other ways must be found to provide the necessary information without revealing the specific chemical component used. The substance class of this agent is entactogenic, which is also sometimes called empatogenic.
MDMA analogue operation
The analogue has an effect on different areas in the brain and on different neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. Changes in mood and perception occur due to changing neurochemistry in various areas.
Increase neurotransmitters (monoamines)
Just like MDMA, the analogue increases serotonin and dopamine levels in the brain by two same mechanisms: stimulating the release and inhibiting the reuptake of these neurotransmitters.
MDMA acts as a substrate for various monoamine vesicular transporter proteins and thereby stimulates the release of serotonin (5HT), dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are stored in small sacs (vesicles) in the nerve endings and are released into the synaptic cleft (the space between the neurons) when an electrical signal is passed. MDMA causes more of these neurotransmitters to be released than normal, causing an excess in the synaptic cleft.
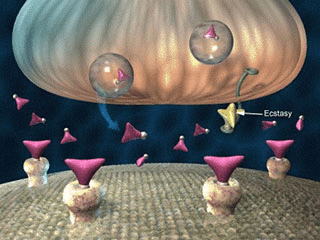
MDMA also reverses the normal transporter flux, increasing the release of all three monoamines via reverse transport. Transporters are proteins located on the cell membrane of neurons that help reabsorb and recycle neurotransmitters after they have passed on their signal. MDMA binds to these transporters and causes them to work in reverse, pushing more neurotransmitters out of the cell instead of taking them back.
Through these two mechanisms, MDMA increases serotonin and dopamine levels in the brain, leading to various psychological and physiological effects. Serotonin influences, among other things, mood, memory, sleep patterns, pain sensation and social behavior. Dopamine plays a role in the reward system, motivation, learning, movement and pleasure. MDMA therefore causes feelings of euphoria, empathy, energy, alertness and increased sensory perception.
Increase neuropeptides
MDMA also increases oxytocin activity by interacting with serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. These serotonergic receptors are widely distributed in the brain, such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex, and influence various functions such as mood, anxiety, cognition and social behavior. Oxytocin is seen as the cuddle hormone because it allows people to connect. Other neuropeptides that are increased are neuropeptide Y, endorphin, dynorphin, vasopressin and BDNF.
Metabolism MDMA analogue
MDMA is metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes, primarily CYP2D6, to form methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). MDA is an active metabolite that also has psychoactive effects and is present in nutmeg. MDMA and MDA are then further metabolized by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and sulfotransferases (SULTs) to form various hydroxylated and sulfated metabolites, such as 4-hydroxy-3-methoxymethamphetamine (HMMA), 3,4-dihydroxymethamphetamine (DHMA) , DHMA 3-sulfate and DHMA 4-sulfate.
The volume of distribution of MDMA is considered large and that means that it spreads throughout the body tissues and does not just stay in the blood. MDMA and its metabolites are excreted mainly via the kidneys, with 75% as unchanged MDMA and 7% as MDA. The half-life of MDMA is approximately 7-9 hours, meaning that it takes approximately that time to remove half of the ingested dose from the body and may even take 48-72 hours before the activity can be considered nil.
The metabolism of MDMA is influenced by several factors, such as the genetic variation of CYP2D6 enzyme activity, the interaction with other drugs that use or inhibit the same enzyme, the dose and frequency of use, and the purity and composition of the drug. MDMA metabolism may also play a role in the drug's potential neurotoxicity, as some metabolites can react with oxygen radicals or other molecules to cause damage to serotonergic neurons.
Recovery time after use
Due to the neurotoxicity and the depletion of various neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, it is advisable to set a recovery time. When using MDMA and its analogues therapeutically, the dosage is not as high as what is seen with recreational use. The higher purity and relatively lower dosage ensure fewer harmful effects. To reverse the depletion of the neurotransmitters, recovery time of at least one month is recommended. For both restoring serotonergic receptors and reducing neurotoxicity, we estimate the best break time between sessions to be between one and two months depending on the user's age and metabolism.
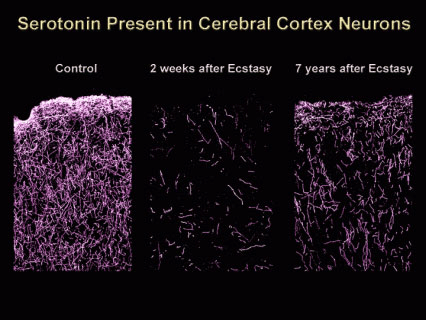
Same risk profile as MDMA
95% Same progression
After ingestion of the MDMA analogue, 95% will function the same as with MDMA. A subtle difference is the slightly longer duration of action and a lower depletion of dopamine compared to MDMA. According to various experts, this makes the MDMA analogue more suitable for therapeutic settings and less suitable as a party drug.
Interactions
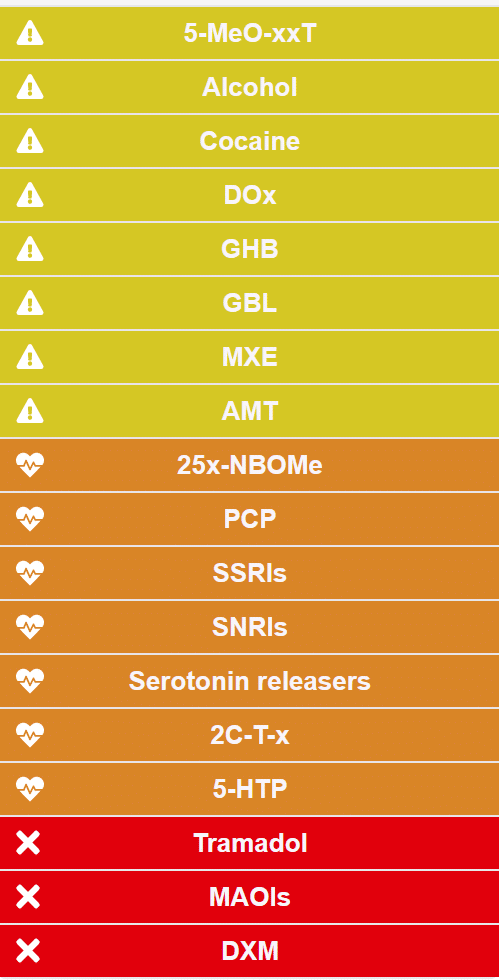
Although MDMA and its various analogues are relatively safe, their use can lead to several unwanted side effects and risks, especially when taken in combination with other drugs or substances. Below is an overview of dangerous interactions for MDMA:
– MDMA in combination with antidepressants can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can lead to severe muscle cramps, fever and delirium.
– Mixing MDMA with alcohol can increase the drug's toxicity, increasing the risk of dehydration and overheating.
– MDMA in combination with other stimulants, such as cocaine, can increase the risk of cardiovascular complications, such as heart palpitations.
– Using MDMA in combination with other drugs such as LSD, magic mushrooms or ketamine can lead to the risk of a bad trip, which can increase psychological stress and anxiety.
Contraindications
There are more contraindications than the above. The use of MDMA is not recommended when taking medication where the drug interacts with the CYP2D6 enzyme, the drugs from the interaction table, heart disease, liver problems, borderline, schizophrenia, psychosis sensitivity and during pregnancies.
Interaction table
Our offer
We can no longer provide analogue as of 01 July 2025. Only when someone brings their own MDMA can we supervise the session. We therefore also no longer offer group sessions with MDMA analogue.
We are not responsible for the quality of self-taken MDMA.
Go through the information below and assess what fits best.
MDMA ceremony
A maximum of five participants and two supervisors are present at an MDMA ceremony. This group session is for those who see added value in the connection of the group.
We can facilitate these when own MDMA is brought.
MDMA session
A MDMA session is guided individually. With more attention to the individual and always a listening ear, an individual session offers more space for expression.
MDMA therapy
MDMA therapy and an MDMA session are different terms for the same thing. At Triptherapie we always offer personal preparation and integration into the process.