New research on psilocybin from 2023
Recent research (publication date September 7, 2023) shows that psilocybin can cause long-term improvements in the immune system of healthy individuals. Depression is seen by more and more specialists as a consequence of inflammatory reactions. Reducing inflammatory products can therefore contribute to depression and anxiety complaints and recovery. The recent study measured significant changes in the inflammatory markers TNF-α, IL-6 and CRP compared to the placebo group.
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection. But if it lasts too long it can cause damage. People become depressed if inflammation levels are high for a long period of time. Depression can prompt individuals to change locations and circumstances. Evolutionarily speaking, depression is an advantage because changing circumstances can lead to better health.
Scientific research has shown that there is a link between inflammatory processes in the body and depression. Several inflammatory markers have been linked to depression, including TNF-alpha, IL-6 and CRP. These are exactly the inflammatory markers that psilocybin has a good influence on. We will provide more explanation for each inflammatory marker
TN-alpha and psilocybin
TNF-alpha, or tumor necrosis factor-alpha, is a cytokine that plays an important role in the body's inflammatory response. It is produced by different types of cells in the immune system and, among other things, acts as a signaling molecule to attract inflammatory cells to the site of infection. TNF-alpha can also increase the expression of other pro-inflammatory genes and thus enhance the inflammatory response.
One of the ways psilocybin works is by regulating the inflammatory response in the body. The latest study has shown that psilocybin can lead to a reduction in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha. This may be an important mechanism for psilocybin's anti-depressant and anti-anxiety effects, as excessive production of TNF-alpha has been linked to depression and anxiety. In addition, psilocybin also has a direct influence on the immune cells that produce TNF-alpha. Furthermore, it has been shown that psilocybin can reduce the activity of these immune cells, reducing the production of TNF-alpha and inhibiting the inflammatory response in the body.
CRP and psilocybin
CRP, or C-reactive protein, is a natural inflammatory marker that increases in response to inflammation and injury in the body. Elevated levels of CRP are associated with several health problems, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis and autoimmune diseases, depression and anxiety.
The new research suggests that psilocybin may have anti-inflammatory properties and could potentially lower CRP levels in the body well after the session.
IL-6 and psilocybin
IL-6 stands for Interleukin-6, also a cytokine, and is a protein that regulates signal transmission between cells. It plays an important role in the immune system and inflammatory processes in the body. IL-6 is produced by different types of cells, such as white blood cells and epithelial cells.
When the immune system is activated by, for example, bacteria, virus oxidation processes or foreign proteins, the production of IL-6 is increased. This helps the body fight the infection.
However, an overproduction of IL-6 can also be harmful. This can lead to chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, there is also a link between increased IL-6 production and psychological disorders such as depression and anxiety. This is because IL-6 can cross the blood-brain barrier and thus influence brain function.
The recent research has shown that psilocybin can reduce the production of IL-6. This study showed that psilocybin reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, even in the long term. This may explain why psilocybin can be effective in treating depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The cortisol peak
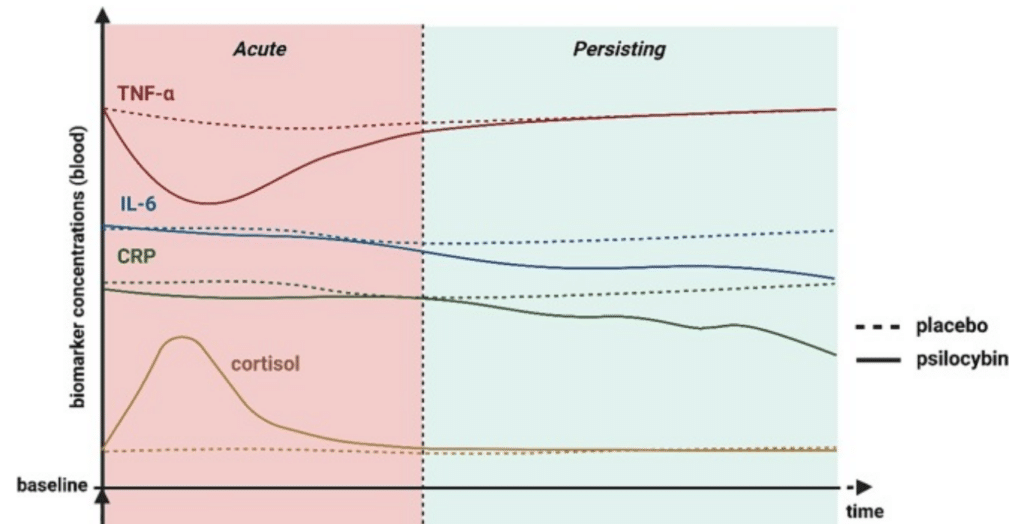
Cortisol is the stress hormone that also suppresses the immune system. During the measurements of the study discussed (see image above), the amount of cortisol increases during the beginning of the session, after which it returns to baseline. This cortisol peak is partly related to the tension one has before a psychedelic trip, supplemented with the necessary response to manipulate the immune system. This explains why some people experience the beginning of psilocybin trips as exciting. In response, the increased activity on the serotonin receptors, especially the 5HT2a variant, as well as other receptors can provide a state of satisfaction. This will allow the stress to disappear.
Less glutamate in the hippocampus
The hippocampus is an important part of the brain involved in memory and emotion. Glutamate is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in this, but too much glutamate can lead to overstimulation of the brain cells, which is associated with anxiety and depression. This is because glutamate activates the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, which in excess can lead to neurotoxicity.
Psilocybin can help to restore this imbalance between glutamate and TNF-alpha. Psilocybin can inhibit the expression of TNF-alpha and can also modulate the activity of the NMDA receptor, thereby reducing the overstimulation of the brain cells. This can lead to a reduction in anxiety and depression.
According to recent research, lowering TNF-alpha has a correlation with a reduced amount of glutamate in the hippocampus. In theory, psilocybin can lower glutamate by lowering TNF-alpha, with the advantage that it inhibits anxiety and depression. However, the correlation can also be interpreted the other way around; Psilocybin reduces the activity of glutamate and therefore also TNF-alpha.
We also previously wrote a post about glutamate in the hippocampus and how it can influence negative experiences during psychedelic sessions. Read more about the role of glutamate and how GABA can help through the button.
Summary of the study
The study showed a reduction in TNF-α during the psilocybin session. Furthermore, IL-6 and CRP showed a significant decrease after seven days compared to the placebo group. The participants noticed long-lasting positive effects after psilocybin. Furthermore, a greater decrease in IL-6 and CRP levels after one week correlated with better mood and social behavior. By reducing the production of inflammatory markers, psilocybin not only potentially alleviates inflammatory responses, but also enhances feelings of connection and positive well-being.
Psilocybin works in more ways
This article only describes a small part of how psilocybin works. Other things include increasing BDNF, neuroplasticity, spiritual experiences and more. Use the buttons below to learn more about the effects of psilocybin.
