BDNF stands for Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor
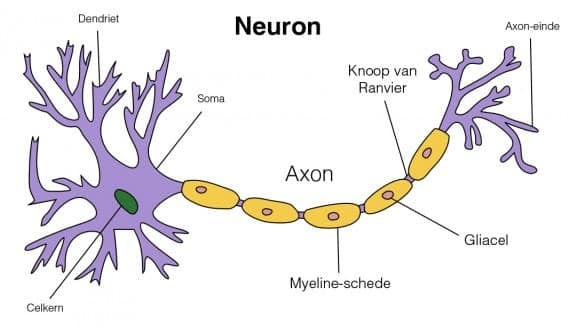
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF, is a neurotrophin. Neurotrophins are important for the survival, repair, and growth of neurons. Neurons are nerve cells that process, transmit, or process information in the brain or nervous system. Neurons can be thought of as the data cables between parts of the brain and the body. An average human body has approximately 100,000,000,000 neurons (100 billion).
Too little BDNF
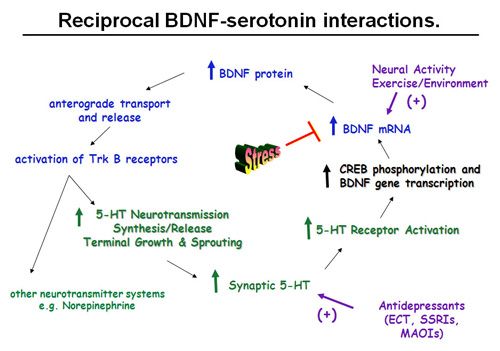
A deficiency of neurotrophins like BDNF contributes to the development of neurodegenerative disorders. A lack of BDNF prevents neurons from repairing damage. This can lead to the development of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and/or Huntington's disease. Furthermore, depression can develop when there is too little BDNF for a prolonged period. The degeneration of neurons in the frontal lobe appears to be the culprit. Low serotonin levels also contribute to depression. Depression is exacerbated because low serotonin levels prevent sufficient BDNF release via the 5-HT2A receptor (see the image below, and note that the 5-HT receptor is stimulated little or not at all).
More BDNF
Producing more BDNF can be achieved by stimulating the 5HT receptor. When the body releases more BDNF, it flips a switch on a series of genes that grow brand-new brain cells and nerve cell connections. Even slightly higher BDNF levels help you learn faster, remember better, age more slowly, and quickly rearrange your brain's connections with different parts of the brain and body.
BDNF also increases your brain's plasticity. When your brain cells are damaged or encounter a stressful situation, BDNF protects them and helps them bounce back stronger. The neural pathways become more flexible instead of broken down, which could explain why higher BDNF levels are associated with fighting off depression.
With a few changes in daily habits, the brain can be programmed to release more and more BDNF, making the brain more resilient and stronger when faced with life's setbacks.
BDNF and serotonin
So, more serotonin leads to increased BDNF release via the 5HT2A receptor. If we're going to look at how to further stimulate the serotonin receptor, we need to consider how to increase serotonin levels and keep the receptor sensitive to stimulation.
Also see our previous post about increase serotonin for more tips
Diet and lower BDNF
The foods below are known to trigger inflammatory responses and lower serotonin, which also lowers BDNF.
Sugar: Eating sugar, and fructose in particular, directly inhibits BDNF production and leads to cognitive decline. Fructose combined with glucose in a single molecule is what we call table sugar. Avoid added sugar as much as possible. Sugar also triggers inflammatory responses in the body, which reduces serotonin release.
Bad fats: Bad fats cause inflammatory reactions in the body, which, through inflammatory factors, reduces serotonin release. These bad fats are typically vegetable omega-6 fats used for frying, such as sunflower, soy, and peanut oil. Hydrogenated (vegetable) fats are also bad fats.
Dairy: Dairy products can also promote inflammation when consumed in high doses. It's best to avoid sweetened or unsweetened dairy products. Unsweetened kefir or yogurt can be eaten in moderation.
Gluten: Eat as few grain-based products as possible. Gluten can also cause inflammation, especially in allergic reactions. Oats and oatmeal are safe to eat.
Alcohol: Alcohol is fermented sugar and is best avoided entirely. If alcohol is consumed, half a glass to a full glass of wine per day can be consumed without too much harm. Above that level, alcohol is already a pro-inflammatory.
Meat: Wild game, grass-fed meat, and wild fish are fine as long as red meat is eaten in moderation (recommended a maximum of twice a week). Any fish that isn't wild-caught or fed anything other than its natural diet is best avoided. Grain- and corn-fed animal products are also discouraged.
Nutrition and higher BDNF
All anti-inflammatory foods and nutrients indirectly help increase BDNF. All antioxidants, polyphenols, and omega-3s therefore boost BDNF. The building blocks of serotonin should also be present in your diet, of course. Below are some BDNF-boosting foods.

Complex carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates are slowly digested and ensure stable blood sugar levels, reducing the need for insulin. This prevents insulin insensitivity and thus various inflammatory responses in the body. Most sources of complex carbohydrates also contain plenty of antioxidants and dietary fiber. It's recommended that half of your daily diet consist of vegetables, along with two pieces of fruit and a small amount of oats. A handful of nuts daily can also have a positive effect on serotonin production.
Omega-3: Omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA play a key role around the serotonin receptor. For example, EPA is an important anti-inflammatory, and DHA makes the cell membrane of the 5HT receptor more sensitive to serotonin. Fish, shellfish, and crustaceans are foods rich in DHA and EPA. Algae and krill also contain high levels of EPA and DHA, and the human body can also synthesize them from the omega-3 fatty acid ALA, which is abundant in flaxseed oil and walnuts (oil).
Omega-6: While we consume an abundance of omega-6 and should limit its intake, GLA (gamma-linolenic acid), an omega-6 fatty acid, can help us combat inflammation. This rare omega-6 fatty acid can be produced in limited quantities by the body. Supplementation is possible with borage oil (Borogo Officinales), evening primrose oil (Oenothera Biennis), or blackcurrant seed oil (Ribis Nigrem).
Polyphenols and antioxidants: Antioxidants, and polyphenols in particular, are very effective against the oxidation of body molecules because they can absorb free radicals such as free oxygen. This prevents inflammation caused by oxidation (like iron rusting). Almost all natural plant foods are packed with polyphenols and antioxidants. The better a food is at absorbing free radicals, the higher its ORAC value, which stands for Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity.
View a list here ORAC values
Tryptophan-rich foods: Tryptophan is the precursor of 5-HTP and serotonin and must therefore be obtained through diet. Foods rich in tryptophan include oatmeal, nuts, seeds, spirulina, cocoa (pure), sesame seeds, chickpeas, spinach, sunflower seeds, parsley, asparagus, mushrooms, broccoli, beans, nuts, seeds, soybeans, and turkey.
Vitamin B: Vitamins B3, B6, and B12 help produce serotonin. Foods that can provide B vitamins include (grass-fed) meat, fish, (acidified) dairy, whole grains, vegetables, fruit, potatoes, legumes, eggs, and (cashew) nuts. A vegan should supplement with B12 because it is only found in animal foods.
Minerals: Minerals such as zinc, iron, and magnesium play an important role in many biochemical processes in the body, including the production of serotonin. Eat as many vegetables as possible, and if you cook them, cook them as briefly as possible. Combine them with as many vegetables as you can. Vary your intake of nuts such as cashews, pistachios, walnuts, and pecans. Cocoa, in its pure, unprocessed form, is very rich in minerals. Whole grains such as brown rice and oats are also good sources of minerals.
MAO inhibitory foods: MAO is an enzyme that breaks down serotonin, among other things. This is a natural process that's supposed to occur. However, certain foods can be used to moderately and healthily inhibit MAO activity, slowing down serotonin breakdown. Seaweed, turmeric, passion flower, and rhodiola are mild MAO inhibitors.
Supplements and BDNF
We previously wrote about supplements that can increase serotonin and therefore BDNF. If diet alone isn't enough, you can also supplement.
View here the serotonin-boosting supplements
Intestinal flora and BDNF
The right nutrients are needed to produce BDNF via serotonin. In your intestines, bacteria predigest many of the important substances for you. Without predigestion, we can't access all the nutrients your body needs. So, first ensure you have the right bacteria in your intestines by taking a probiotic containing one or more of the following strains: Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei and Bifidobacteriumbifidum. Then you give those bacteria and yourself the right nutrition and dietary fiber from mainly vegetables, legumes, moderate fruits and some whole grain products such as oatmeal.
Exercise and BDNF
Cardio training stimulates the production of a protein called FNDC5 (ibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5). FNDC5, in turn, increases BDNF by 200-300 %. This increase is long-lasting. In a study of men who cycled daily for three months, BDNF levels almost quadrupled.
Regular strength training also increases BDNF, but this only lasts for a few minutes after the workout. A better form of training is interval training or any other type of exercise that alternates between high intensity and rest.
Sleep and BDNF
Deep sleep triggers the release of DMT, which is similar to serotonin and therefore also activates the 5HT2a receptor. This causes the body to release BDNF during the deeper stages of sleep. There are four sleep stages that repeat every 90 minutes. On average, you spend about a third to half of your night in stages 3 and 4. DMT and BDNF activity are highest during these stages.
Meditation and BDNF
Meditation reduces stress and therefore increases BDNF. A good, deep meditation tricks the body into thinking it's asleep and releases DMT. By stimulating the 5HT2a receptor, DMT promotes the release of BDNF. The same applies to breathing techniques, which make the body appear to be asleep.
Sunlight and BDNF
Sun exposure increases BDNF by increasing vitamin D. It also improves mood and actually reduces your risk of skin cancer, provided you don't burn. Get outside in direct sunlight for fifteen minutes a day. Unfortunately, the sun isn't strong enough in winter. Supplementing with vitamin D or eating fatty fish, liver, cheese (the least good choice), or egg yolks can help you get vitamin D in winter.
Social contact and BDNF
A lack of meaningful mental stimulation leads to lower BDNF levels. Social isolation also contributes to depression, which decreases BDNF. Reduce your social media use and connect in person. Conversations with strangers are very beneficial for BDNF and leave you feeling good afterward.
Psychedelics and BDNF
Psychedelics increase BDNF production and neurogenesis. This explains the recent surge in research on psychedelic-assisted therapy for depression and PTSD.
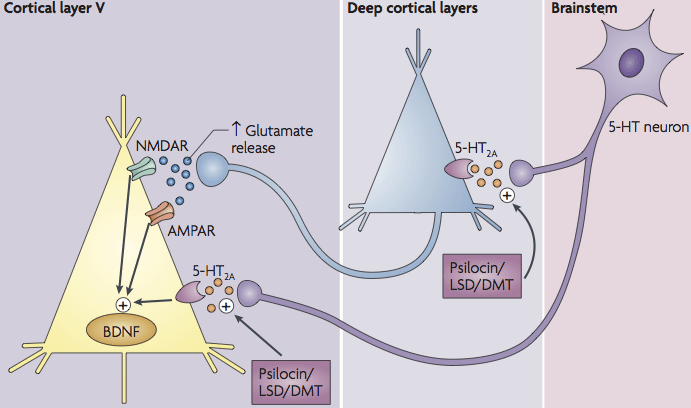
The highest possible stimulation of the 5HT2a receptor to release BDNF is the use of psychedelics. These are truly mind-altering drugs (English for medication). Psilocin from magic mushrooms, DMT from ayahuasca, or LSD stimulate the 5HT2a receptor so that BDNF also increases significantly. This combination leads to neurogenesis, which means the creation of new neurons, at an unprecedented level.
Our trip therapy and BDNF
In our trip therapy, we use psilocybin-containing mushrooms or magic truffles. After being converted into psilocin by the body, psilocybin causes a very high stimulation of the 5HT-2a receptor. This stimulation, along with the release of BDNF due to the stimulation of the 5HT2a receptor, causes the brain to enter a state of hyperconnectivity (see image).
During this state of hyperconnectivity, neurogenesis occurs and the conscious mind connects with the subconscious. This can resolve problems in the subconscious, reducing stress, which BDNF inhibits. New permanent connections are also created, and repair processes take place to repair the damage caused by depression. Even neurodegenerative diseases can be combated by BDNF activity, as new neurons and thus connections are created.
Support from us
It's clear that psilocybin is a very powerful and natural remedy for neurodegenerative diseases and depression. A high level of stimulation from psilocybin is called tripping, and hallucinations can occur at higher doses. For the most effective experience, it's highly recommended to hire a professional trip sitter or therapist. See who's available via the button.
References used:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3022308/
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/expphysiol.2009.048512/full
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095254614001161
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27385735
http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0076050
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25584253
http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v16/n4/full/nrn3916.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24705269
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4104707/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23727882
http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v11/n9/fig_tab/nrn2884_F1.html
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jphs/91/4/91_4_267/_article
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4104707/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23312069
http://file.scirp.org/pdf/FNS_2013083011411606.pdf
http://www.jneurosci.org/content/30/38/12653
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3977651/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3487856/
https://academic.oup.com/jnci/article/97/3/161/2544132/Sunlight-and-Reduced-Risk-of-Cancer-Is-The-Real
http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0076050
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25584253
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2694409/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3448146/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11119686
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16533499
